Marketers need to upgrade existing products or develop new product to
maintain an edge over competitors. New product development can be risky at
times, if the product is not accepted by the markets. New product fails due to
many reasons like not having a good design, improper positioning, higher cost
and competitor relations. Therefore, there must be proper coordination among
the various departments of a company to ensure a new product’s success.
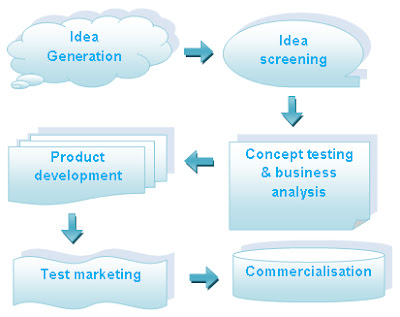
Organisation follows various steps for new product development. They are:
- Idea generation: there are various sources from where companies can get ideas for new product development. The source can be top management, customers, scientists, competitors, employee and even channel members. Generally, product managers are encouraged to take risk and come up with new ideas for development of new product.
- Ideas screening: All ideas can not be implemented because of various difficulties. Therefore, there has to be a screening process. Companies appoint committees, who divide ideas into three groups: Promising ideas, marginal ideas and rejects. Promising ideas are studied further for feasibility. The basic aim of screening is to drop poor ideas.
- Concept testing and business analysis: the most attractive idea, which passes the initial screening stage, proceeds to the next stage i.e. concept testing. A product concept is the idea expressed in meaningful terms. At this stage, the idea is sent for external evaluation and feedback is sought. The result of concept testing helps understand the benefits that customers will look for in a product. Top management must evaluate the product’s business attractiveness through business analysis. This is an in-depth financial evaluation of the proposed new product.
- Product development: after the product clears the business analysis stage, it is sent to the research and development (R & D) or engineering department for converting into a physical product. This stage calls for huge investment, so at this point, the company should determine if the product is technically and commercially feasible. More than one prototype attributes is selected. The prototype then undergoes customer tests. It takes quits some time to develop a successful prototype.
- Test marketing: after passing physiological and functional performance tests, the product is branded and packaged for test marketing. The idea of the marketing is to observe the reaction of consumers and/dealers towards handling, using and repurchasing the product. Market research is affected by the investment costs, risk, time constraints and cost of research.
- Commercialisation: In this stage, the product enters the market. But, before this the results of the test marketing help frame the right marketing mix. The firm incurs heavy expenditure during this stage as it goes for large scale production.
All the above steps, when followed in an organised manner lead to
successful new product development.

No comments:
Post a Comment